- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-05-10 Origin: Site








Are you wondering which material is best for your next high-performance project? Billet and cast materials are both crucial in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical. In this article, we'll explore the key differences between these materials, focusing on billet plate and its advantages over cast alternatives. You'll learn how the choice between billet and cast affects manufacturing efficiency, strength, and cost.
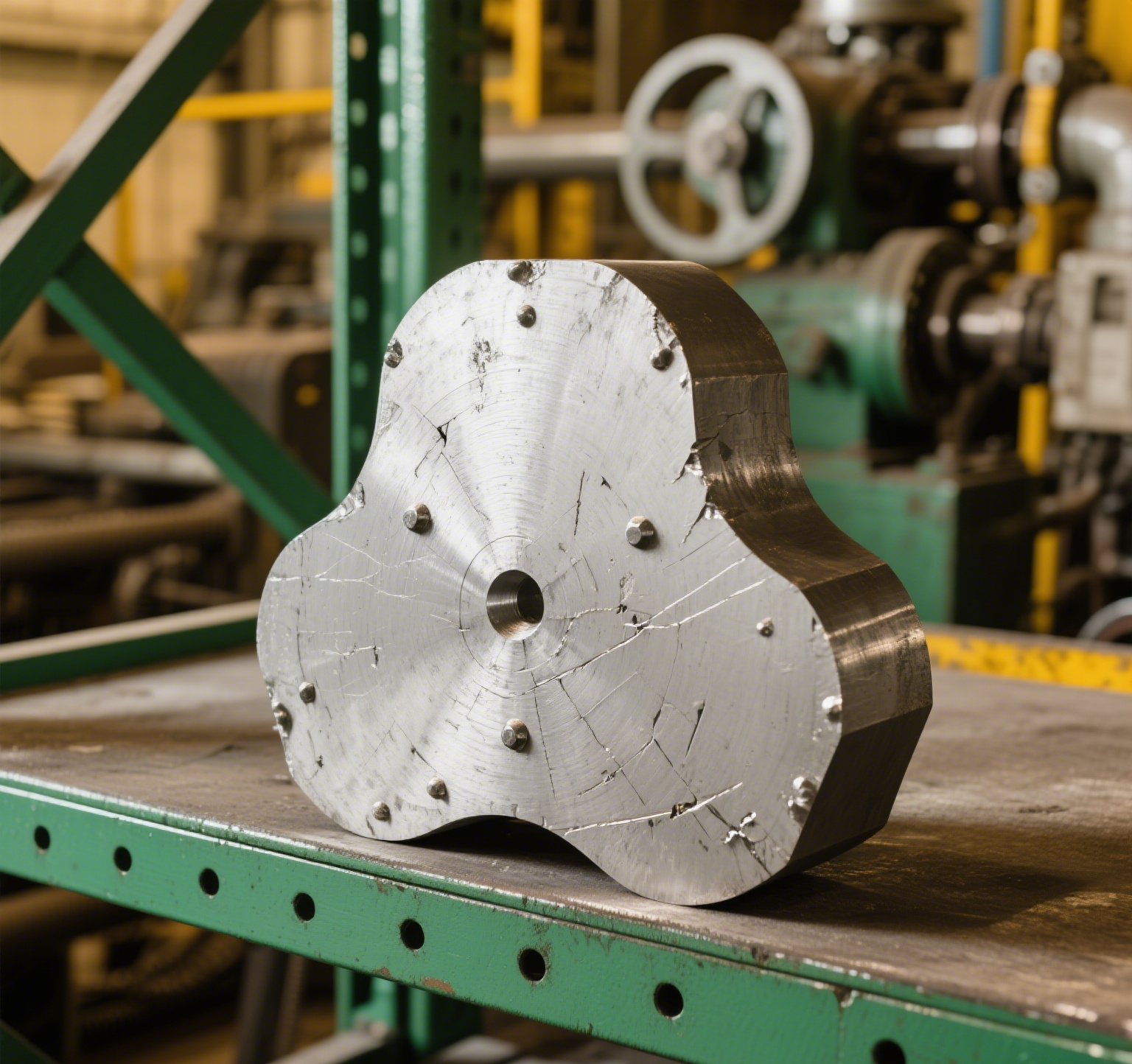
A billet plate is a solid, compact piece of metal, typically characterized by its uniform structure and high strength. It is often processed further through machining to create precision parts. Billet materials are ideal for industries that require high-performance, durable components.
Aerospace: Critical components like turbine blades.
Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, implants.
Automotive Components: Racing parts, high-performance engine components.
Precision Instruments: Parts requiring fine tolerances.
Cast materials are created by melting metal, such as aluminum or steel, and pouring it into molds. Once the metal cools, it solidifies into the desired shape. This method is great for producing complex shapes but may lead to porosity in the final product.
Engine Blocks: Common in automotive and machinery.
Transmission Housings: Components that need intricate designs.
High-Volume Production Parts: Often used for large quantities of identical components.
The key difference between billet and cast materials lies in the manufacturing method. Billets are created from solid blocks of metal, resulting in stronger, more durable products. In contrast, casting uses molten metal poured into molds, allowing for complex geometries but at the cost of reduced strength due to potential porosity.
| Feature | Billet Material | Cast Material |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Solid metal shaped through machining | Molten metal poured into molds |
| Strength | High, uniform structure | Moderate, with possible porosity |
| Applications | Precision parts, high-performance | Complex shapes, mass production |
| Cost | Higher cost, ideal for low volumes | More cost-effective for high volume |
The decision between these materials largely depends on the required strength, the complexity of the part, and production volume.
Continuous Casting:
The process starts with molten metal being continuously poured into molds. As it cools, it solidifies into a billet. This ensures a uniform density and solid structure, which is crucial for high-performance materials like billet plates.
Hot Rolling:
Once solidified, the billet undergoes hot rolling. This step shapes the billet into specific dimensions, resulting in billet plates with the desired width and thickness. The rolling process helps refine the material for its intended use.
Machining from Billets:
After the billet is rolled, it is often machined using CNC technology. This allows for tight tolerances and precision, essential for creating parts like aerospace components, medical instruments, and custom automotive parts from billet plates.
Sand Casting:
In this method, molten metal is poured into a sand mold and allowed to cool. It’s cost-effective and versatile but can leave rough surfaces that require post-processing. This is often used for parts like engine blocks or large industrial components.
Die Casting:
For high-volume production, molten metal is injected under high pressure into a metal mold. This method is highly efficient and is used for parts like engine blocks and transmission housings. Die casting is ideal for mass production but may result in slightly lower strength due to the method's cooling rate.
Investment Casting:
This process involves creating a mold around a wax pattern. Once the mold is set, the wax is melted out, leaving behind the precise shape of the part. This method is often used for parts requiring intricate details or complex shapes, such as turbine blades in the aerospace industry.
| Step | Billet Manufacturing | Casting Process |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Continuous casting and hot rolling | Sand casting, die casting, investment casting |
| Material State | Solid block (billet) | Molten metal |
| Precision | High precision through machining | Moderate precision, depends on method |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical, automotive | Engine blocks, housing components, industrial parts |
This table shows how the methods differ in their approach, material state, and precision. Each method has its place depending on the type of part being produced.
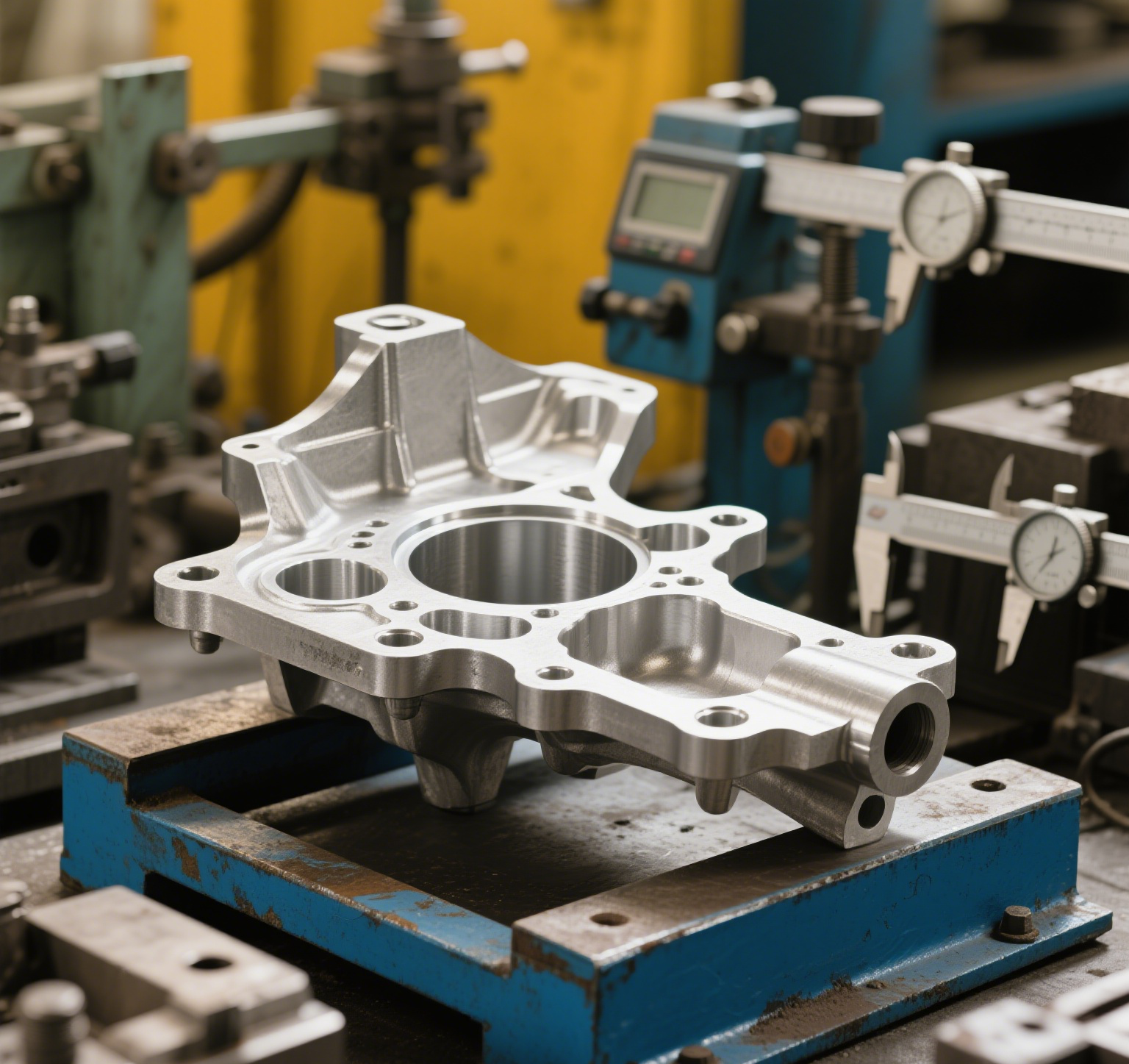
Billet Plate:
A billet plate is solid and compact, ensuring minimal defects and a uniform grain structure. This results in a stronger and more reliable material, perfect for demanding applications.
Cast Plate:
Cast plates can have irregular grain structures, and sometimes, internal voids or porosity may form. This can affect the overall integrity of the material, making it less durable in high-stress conditions.
Billet Plate:
Thanks to the uniform structure, billet plates offer higher tensile strength. This makes them ideal for applications requiring toughness, such as aerospace components and medical devices where reliability is crucial.
Cast Plate:
Cast plates generally have lower strength because of potential porosity. However, casting allows for more complex shapes, which is useful in automotive and consumer products that require intricate designs but less focus on maximum strength.
Billet Plate:
Billet plates usually have a smoother finish straight out of the manufacturing process, minimizing the need for post-processing. This is especially valuable when a precise surface finish is essential for parts.
Cast Plate:
Cast plates tend to have a rougher finish after casting, which often requires additional machining or polishing. This makes them suitable for mass-produced parts where the finish isn’t the top priority.
Billet Plate:
Due to the need for CNC machining and tight precision, billet plates are generally more expensive, especially in low-volume production. The higher cost is justified by the superior material quality.
Cast Plate:
Cast plates are more cost-effective, especially in large-scale production. While tooling and setup costs can be high, the per-unit cost decreases significantly when producing large quantities.
Billet Plate Applications:
Aerospace: Used for high-strength components like turbine blades.
Medical Devices: Surgical instruments and implants.
High-Performance Automotive Parts: Such as engine components and custom car parts.
Precision Instruments: Parts that require tight tolerances.
Cast Plate Applications:
Automotive: Commonly used in engine blocks, transmission housings, and other parts.
Industrial Equipment: Components requiring complex shapes, such as pumps and machinery parts.
Consumer Products: Furniture components, lamps, and other household items.
| Feature | Billet Plate | Cast Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Solid, compact, uniform grain | Irregular grain, potential porosity |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Lower strength, but complex shapes possible |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, minimal post-processing | Rough, requires further machining |
| Cost | Higher cost per unit, low volume | Lower cost per unit, high volume |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical, high-performance automotive | Automotive, industrial, consumer goods |
This table highlights the main differences in structure, strength, finish, and cost between billet plates and cast plates, helping you decide which is more suitable for your needs.
Strength Requirements:
If you need a material that can withstand high stress and pressure, billet plates are the better choice. Their uniform structure provides superior strength and durability, making them ideal for critical applications like aerospace and medical devices.
Cost and Volume:
If your project focuses on cost-effectiveness and large production volumes, cast plates may be more suitable. While they may lack the strength of billet, they excel in mass production and offer significant savings for high-volume orders.
Complexity of the Part:
When your parts require intricate shapes or complex geometries, casting is the way to go. Cast plates are perfect for items like engine blocks or industrial machinery components. However, if precise dimensions and uniform properties are crucial, billet is the best choice.
Aerospace:
Billet materials are commonly used in aerospace for high-performance parts like turbine blades and structural components that need both strength and precision.
Medical Devices:
Surgical instruments, implants, and other medical components require the high strength and uniformity that billet plates provide.
Precision Instruments:
Parts needing tight tolerances, such as measurement devices, are typically made from billet due to its superior finish and machining capabilities.
Custom, High-Performance Parts:
Billet plates are ideal for creating custom parts in racing, automotive, and other high-performance applications where structural integrity is critical.
Automotive Components:
Cast materials are widely used for manufacturing engine blocks, transmission housings, and other automotive components that need complex shapes and large-scale production.
Consumer Goods:
For mass-produced consumer items like furniture components or light fixtures, cast plates offer a cost-effective solution while allowing for intricate designs.
Industrial Machinery:
Cast materials are perfect for industrial machinery parts, such as pumps or housings, where high-volume production and complex geometries are required.
| Factor | Billet Plate | Cast Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate strength, lower durability |
| Cost | Higher cost, ideal for low volumes | Lower cost, ideal for high volumes |
| Complexity | Best for parts requiring precision | Best for parts with complex shapes |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical, high-performance | Automotive, industrial, consumer goods |
This table summarizes the key factors to help you choose between billet plates and cast plates, depending on your project’s requirements.
In some applications, manufacturers use a hybrid approach by combining the advantages of both casting and billet materials. For example, a component may be cast to form the basic shape, but then machined from a billet plate to refine critical features. This allows for complex geometries to be created through casting, while maintaining the precision and strength needed for high-performance parts.
A common example of this hybrid approach is seen in turbocharger components, where the base structure is cast, but critical surfaces are machined from billet to ensure tighter tolerances and better durability.
Forged aluminum and billet aluminum are both strong materials used in various high-performance applications. However, there’s a key difference in how they are made and their strength properties.
Billet Aluminum:
Billet aluminum starts as a solid block, which is machined into the final part. The machining process gives billet plates a smooth surface and precise dimensions. It’s known for its consistent strength, making it suitable for parts that require tight tolerances.
Forged Aluminum:
Forged aluminum is made by applying high pressure to the material, which shapes it into the final form. The forging process compresses the metal, making it denser and stronger. This gives forged aluminum higher tensile strength compared to billet aluminum, making it ideal for parts that will face heavy loads or extreme stress, such as in aerospace or heavy machinery.
| Feature | Billet Aluminum | Forged Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Machined from solid blocks | Shaped under high pressure |
| Strength | High, uniform strength | Higher strength due to compression |
| Applications | Precision parts, automotive | Aerospace, heavy machinery, racing |
| Cost | Higher cost, low volume | Cost-effective for large volumes |
This comparison highlights the differences in strength and manufacturing methods between billet and forged aluminum, showing how each is suited for specific needs.
Billet Materials:
Billet plates are typically machined from solid blocks of metal, which can result in significant material scrap. However, advancements in modern machining technologies, like more precise cutting and recycling methods, can help reduce waste. Still, the need for precision often leads to more material loss compared to casting.
Cast Materials:
One of the benefits of casting is the ability to recycle excess material. After a part is cast, any unused metal can often be melted down and reused for future casting. This reduces waste and supports sustainability in the production process.
Billet Manufacturing:
The process of producing billet plates typically requires higher energy consumption, especially due to the machining involved. CNC machines and other precision equipment require significant power to achieve the necessary accuracy and finish. This makes billet production more energy-intensive, particularly when high precision is needed.
Casting:
Casting tends to be more energy-efficient for mass production. Especially in high-volume operations like die casting, molten metal is poured into molds, and the cooling process is less energy-consuming compared to the precision machining required for billets. While initial setup and tooling can be expensive, casting operations benefit from lower energy use once in full production.
| Factor | Billet Manufacturing | Casting Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Generation | High scrap due to machining | Lower waste, recyclable excess material |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use for precision machining | More energy-efficient for mass production |
This comparison highlights the environmental impact of both manufacturing methods, showing how billet and cast processes differ in terms of waste and energy use.
In aerospace, billet plates are the go-to choice due to their superior strength and precision. Billet plates offer the high tensile strength needed for critical aerospace components like turbine blades and structural parts. These parts must endure extreme stresses, so the uniform grain structure of billet materials is crucial for reliability.
On the other hand, cast materials are typically used for larger, less precise components, such as housing and casing parts. While these parts don't require the same level of precision, casting is more cost-effective for producing high-volume components like these.
Billet plates are commonly found in high-performance racing components, such as custom engine parts and suspension components. The high strength and precision of billet materials make them ideal for parts that need to withstand extreme conditions and tight tolerances, where every fraction of a millimeter counts.
Cast materials, however, are more suitable for mass production. Engine blocks and transmission housings are typically made from cast materials, as these parts don't require the same level of precision and can be produced more efficiently at lower cost.
| Application | Billet Plate | Cast Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, structural parts | Housing, cases |
| Automotive | High-performance racing components | Engine blocks, transmission housings |
This table illustrates how billet plates are favored for high-performance applications that require precision, while cast plates are more suited for mass-produced, less intricate parts.
Billet plates are known for their high strength, uniform structure, and precision. They are ideal for applications that require durability and tight tolerances, like aerospace and medical devices. Cast materials, on the other hand, are more cost-effective for mass production and complex shapes but may have lower strength due to porosity.
When choosing between billet plates and cast materials, consider factors like performance, production volume, and cost-effectiveness. For high-performance, precision parts, billets are the best option, while cast materials are suitable for large-scale production.
Copyright © 2023 Ningbo Chuangrun New Materials Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. | Sitemap | Privacy Policy | Support By Leadong